Torque Specifications for Standard Bolts and Nuts
Hexagon Bolt (7T) and general Nut information:
1. M6 x 1.0mm
•87 – 104 in-lb (9.8 – 11.8 N m, 1.0 – 1.2 kgf m)
2. M8 x 1.25mm
•200 – 251 in-lb (22.6 – 28.4 N m, 2.3 – 2.9 kgf m)
3. M10 x 1.5mm
•430 – 505 in-lb (48.7 – 57.1 N m, 5.5 – 5.8 kgf m)
4. M12 x 1.75mm
•780 – 908 in-lb (88.4 – 102.6 N m, 9.0 – 10.4 kgf m)
5. M14 x 1.5mm
•1130 – 1347 in-lb (127.5 – 152.1 N m, 13.5 – 15.4 kgf m)
6. M16 x 1.5mm
•1915 – 2047 in-lb (215.7 – 231.4 N m, 22.0 – 24.0 kgf m)
PT Plug:
1. 1/4 in
•87 in-lb (9.8 N·m, 1.0 kgf·m)
2. 3/8 in
•173 in-lb (19.6 N m, 2.0 kgf m)
3. 1/2 in
•260 in-lb (29.4 N m, 3.0 kgf m)
Comments:
•Apply 80% of the value when the mounting part is aluminum.
•Apply 60% of the value for 4T bolts and locknuts.
•For bolts not listed, apply 60% torque.
•Apply 80% torque when tightened on aluminum alloy.
Additional Information for Cylinder Head Reassembly
Squareness
• Procedure: Use a flat surface and a square to check each spring for squareness.
• Reference: Figure 6-22
Free Length
• Procedure: Use a caliper to measure the length of the spring.
• Reference: Figure 6-23
• Service Limit: See Valve Spring on page 6-5 for the service limit.
Reassembly of the Cylinder Head
• New Components: Use new gaskets, O-rings and seals when reassembling the cylinder head.
IMPORTANT: Liberally lubricate all components during assembly to prevent premature wear or damage.
Reassembly of Valve Guides
1. Installation:
•The valve guides are mounted in the cylinder head with a very tight press fit.
• Preparation: Place the valve guides in a freezer for at least twenty minutes before installing them. This causes the valve guides to shrink, making them easier to install.
2. Reinsertion:
•Immediately after removing the valve guides from the freezer, remove the valve guides and place them in the correct position.
• Reference: Figure 6-24 (1)
Further Instructions for Cylinder Head Reassembly
Cylinder Head Installation Steps:
5. Cylinder head preparation:
•Place the cylinder head combustion side down on the workbench to install the valve springs.
• Reference: Reinstall the valve spring (Figure 6-28, (4)) and valve spring retainer (Figure 6-28, (5)).
6. Compression of the Valve Spring:
•Use a valve spring compression tool to compress the valve spring.
7. Installation of Valve Keeper and Valve Cover:
•Install the valve keeper (Figure 6-28, (2)) and slowly release the tension in the valve spring.
•Reinstall the valve cover (Figure 6-28, (1)).
•Repeat these steps for all remaining valves.
Reassembly of the Cylinder Head:
1. Cleaning:
•Carefully clean both the combustion surface of the cylinder head and the top of the cylinder block.
•Install a new cylinder head gasket (Figure 6-29, (2)) on the cylinder block.
2. Positioning:
•Place the cylinder head on the cylinder head gasket.
3. Cylinder head bolts:
•Lightly lubricate the threads of the cylinder head bolts (Figure 6-29, (1)).
•Tighten the bolts to the specified torque as stated in the table.
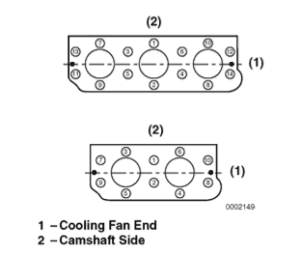
•Tighten in the order shown in Figure 6-30.
Tightening Sequence and Steps:
• Torque Sequence: Follow the pattern shown in Figure 6-30.
•1 = Cooling fan side
•2 = Camshaft side
• Tightening steps:
1.First Step: 1/2 of the final torque
2.Second Step: Final torque
Reference for Torque: See Torque for Nuts and Bolts on page 6-13.
These additional instructions complete the cylinder head reassembly process, ensuring that each part is properly installed and torqued to specification, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the engine components.
Adjust valve clearance
At the heart of a well-running Yanmar engine lies a carefully adjusted valve mechanism. The story of adjusting these valves begins with a deep understanding of the sequence and accuracy required to ensure optimal engine performance.
Order of Adjustment
Imagine you’re working on a rugged Yanmar engine. The number 1 piston, your starting point, is on the flywheel side of the engine. With a 3-cylinder engine you must follow the firing order 1-3-2, while a 2-cylinder engine uses the order 1-2. In a 3-cylinder engine, each ignition occurs after every 240 degrees of crankshaft rotation. In contrast, a 2-cylinder engine has unequal ignition, with the second cylinder firing 180 degrees after the first.
Checking and Adjusting Valve Clearance
Now that you know the basic sequence, it’s time to check the valve clearance. Both the intake and exhaust valves should be checked when the piston is at top dead center (TDC) of the compression stroke. The correct valve clearance is measured with a feeler gauge that you place between the valve stem and the rocker arm.
Procedure
1. Preparation :
•Remove the intake manifold and valve cover.
•Turn the crankshaft clockwise to bring the number 1 piston to TDC.
2. Measuring and Adjusting :
•Place a feeler gauge of appropriate thickness between the rocker arm and the valve stem cap.
•Turn the valve screw to adjust the valve clearance until there is a slight “drag” on the feeler gauge when it is slid between the rocker arm and the valve stem cap.
3. Loosening the Valve Screw Locknut :
•Loosen the valve screw locknut and turn the valve screw to set the correct valve clearance.
•Check the valve for any tilt, dirt or wear.
4. Fixing and Rechecking :
•Hold the adjustment screw while tightening the valve screw locknut.
•Recheck the valve clearance, as the clearance tends to decrease slightly when the locknut is tightened. It is advisable to make the initial adjustment slightly on the “loose” side.
5. Finishing :
•Apply oil to the contact surface between the adjustment screw and the push rod.
•Turn the crankshaft and measure the next cylinder. Repeat this process until all valves are adjusted.
Visual Support
The images in the manual will help you with every step of the process. They clearly show how to install the feeler gauge, how to loosen and retighten the valve screw locknut, and where to apply oil. This visual guidance is crucial to ensure that you follow the procedure accurately and that the engine continues to perform optimally.
By following these steps carefully, you will ensure that the Yanmar engine valves are adjusted correctly, leading to smooth and efficient engine operation. It’s a delicate process that requires accuracy and attention to detail, but the reward is a high-performing engine that remains reliable and powerful.
The technical data
2TNV70
Here is the table with the technical data of the 2TNV70 engine:
| Technical Overview 2TNV70 | Details |
|---|---|
| Motorcycle model | 2TNV70 |
| Version | VM |
| Type | Vertical Inline Diesel Engine |
| Combustion system | Ball-type Swirl Chamber |
| Aspiration | Naturally |
| Amount of cilinders | 2 |
| Bore x Stroke | 70x74mm |
| Cylinder capacity | 570 cc (0.570 L) |
| Continuous Rated Power | |
| 3000 RPM | 10.9 hp (8.1 kW) |
| 3600 RPM | 13.1 hp (9.7 kW) |
| Maximum Rated Power (Net) | |
| 3000 RPM | 12.3 hp (9.2 kW) |
| 3600 RPM | 14.3 hp (10.7 kW) |
| Idle speed | |
| High idle | 3000-3200 RPM (3000 RPM min. ±25) |
| Low idle | 850RPM |
| Engine Weight (Dry) | 182.2 lbs (84 kg) |
| PTO Position | Flywheel side |
| Direction of rotation | Counterclockwise, as seen from the flywheel side |
| Cooling system | Liquid cooled with radiator |
| Lubrication system | Forced lubrication with trochoid pump |
| Normal Oil Pressure at rated speed | 42 – 64 PSI (2.96 – 4.49 kgf/cm²) |
| Normal Oil Pressure at low idle speed | 8.5 PSI (0.6 MPa, 0.6 kgf/cm²) or more |
| Starting system | |
| Electric starter motor | DC12V, 1.3 hp (1.0 kW) |
| Alternator | DC12V, 20A |
| Recommended battery capacity | 12V, 36 Ah (5h rating) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 416 x 427 x 484mm |
| Engine oil capacity | |
| With oil filter | 1.7 / 0.8 L (Dipstick above/below limit) |
| Engine coolant capacity | 1.6L |
| Standard Cooling Fan | 10.23 inches (260.0 mm), 5 Blade Pusher Type |
| Valve clearance | |
| Inlet | 0.17mm |
| Exhaust pipe | 0.72mm |
3TNV70
| Technical Overview 3TNV70 | Details |
|---|---|
| Motorcycle model | 3TNV70 |
| Version | VM, CH, VH |
| Type | Vertical Inline Diesel Engine |
| Combustion system | Ball-type Swirl Chamber |
| Aspiration | Naturally |
| Amount of cilinders | 3 |
| Bore x Stroke | 70x74mm |
| Cylinder capacity | 854 cc (0.854 L) |
| Continuous Rated Power | |
| 3000 RPM | 16.7 hp (12.5 kW) |
| 3600 RPM | 19.4 hp (14.5 kW) |
| Maximum Rated Power (Net) | |
| 3000 RPM | 18.5 hp (13.8 kW) |
| 3600 RPM | 21.7 hp (16.2 kW) |
| Idle speed | |
| High idle | 3000-3200 RPM (3000 RPM min. ±25) |
| Low idle | 850RPM |
| Engine Weight (Dry) | 192.1 lbs (87 kg) |
| PTO Position | Flywheel side |
| Direction of rotation | Counterclockwise, as seen from the flywheel side |
| Cooling system | Liquid cooled with radiator |
| Lubrication system | Forced lubrication with trochoid pump |
| Normal Oil Pressure at rated speed | 42 – 64 PSI (2.96 – 4.49 kgf/cm²) |
| Normal Oil Pressure at low idle speed | 8.5 PSI (0.6 MPa, 0.6 kgf/cm²) or more |
| Starting system | |
| Electric starter motor | DC12V, 1.3 hp (1.0 kW) |
| Alternator | DC12V, 20A |
| Recommended battery capacity | 12V, 36 Ah (5h rating) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 498x508x506mm |
| Engine oil capacity | |
| With oil filter | 3.0 / 1.6 L (Dipstick above/below limit) |
| Engine coolant capacity | 0.92 gal (3.5 L) |
| Standard Cooling Fan | 12.20 inches (310.0 mm), 5 Blade Pusher Type |
| Valve clearance | |
| Inlet | 0.17mm |
| Exhaust pipe | 0.72mm |
3TNV76
General information
4o